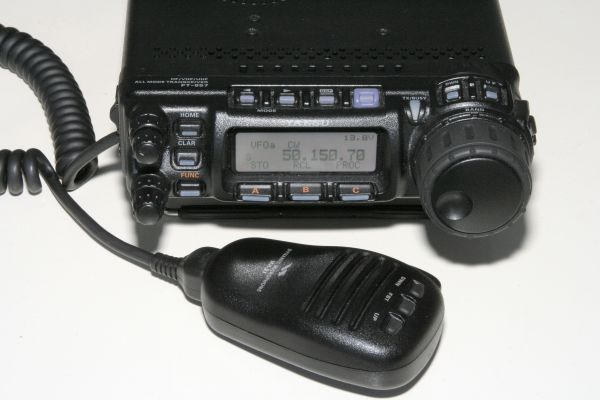

All amateur radio equipment is a compromise to some extent, the FT857D is no exception. While I had been prepared to accept some of the shortcomings of the rig, one that became a real problem were high power "spikes" when using the rig on low power - this may not be an issue when running the rig at 100 Watts output on CW and SSB.
The ARRL and RSGB reviews of this rig didn't show a problem, yet speaking with other users would suggest many FT857 and FT897 transceivers also suffer from this issue. In the case of my transceiver the effect seems most noticeable in the mid HF frequency bands and is present on CW, SSB and AM. For those who use AM, the spike can be horrific and exceeds 100 Watts out when the microphone PTT is first pressed. SSB doesn't fare any better with spikes occurring on the first syllable spoken after a pause. The spikes on SSB exceed 100 Watts when the power level is set to 10 or 20 Watts. While my concerns are for the welfare of my linear amplifier, the interference potential is significant.
Running the FT857 "barefoot" doesn't give any indications on the front panel of a problem, and indeed in many cases there isn't an issue with doubling your power for the first 5 milliseconds on transmit. Where this can be a serious issue is using the FT857 to drive other equipment, such as a linear amplifier. Fortunately my Acom 1000 linear is rated to cope with spikes of up to 100 mS duration, and these are less than that. Users of other types of amplifier may damage their equipment.
Examples of the first CW character being sent are shown below, the power output setting was 20 Watts on the 7 MHz band.
The only cure I've found so far is to feed a fixed voltage of between -3.0 and -3.5 Volts into the ALC socket of the FT857. Using a fixed ALC voltage still allows the power output to be set correctly from the menu in the FT857, it is also beneficial in taming the SSB spikes without causing problems to normal speech peaks.
Not all bands produce the same results, the spikes were at their worst in the mid HF bands and almost non existent on 2m. As my oscilloscope is not capable of working at 432 MHz, I cannot comment on that band.
From my experimentation, feeding what appears to be a reasonable voltage level on one band can reduce the power output on another band to near zero. This indicates that setting the voltage could be quite critical. I haven't tried the transceiver at widely differing case temperatures, nor have I tried any other transceivers to see if using the voltage my transceiver works well with also has the same effect on a another 857.
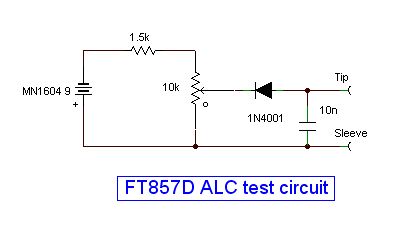
The test circuit I used is shown below, using a 9 Volt alkaline battery is not a good choice as the maximum voltage required is only -4 Volts. The output (tip and sleeve) are wired to a 3.5mm jack plug, which is inserted into the ALC input socket on the FT857D. The 1.5 K Ohm series resistor avoids shorting the battery out when inserting the jack plug into the transceiver. For longer term use, 3 or 4 AA sized alkaline batteries would be a more sensible source of the voltage. Note the FT857D manual gives an ALC input range between 0 and -4 Volts in the specifications. The optimum ALC voltage feed on my transceiver was -3.1 Volts, this level still allowed full output on 2 metres. A setting of -3.6 volts worked well on HF and 6 metres, but killed the output completely on 2metres.
 |
 |
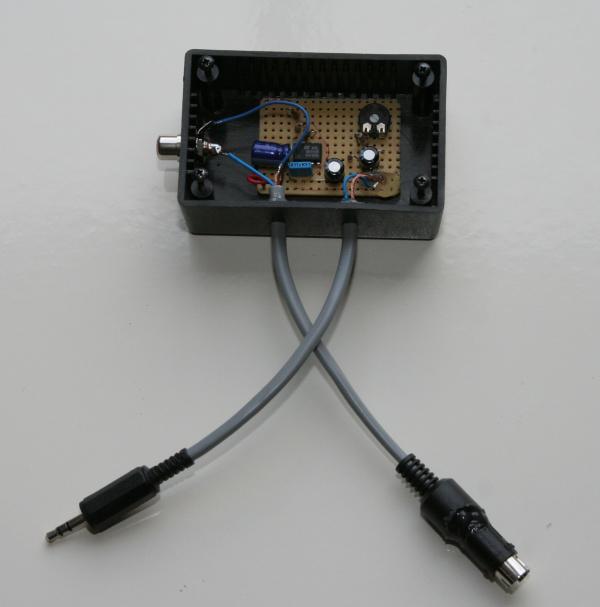
A more elegant solution is to generate a negative voltage by the use of an NE555, as shown below. A 13.8 volt supply is available from the "linear" socket on the FT857. Be careful when wiring a mini DIN plug as they are quite small and tricky to solder without creating a short. Covering the rear of the pins with hot melt glue after soldering the wires helps keep everything secure and short free - the plastic glue can be peeled off for re-work without difficulty. The photo of the completed box also has a phono socket connected to the TX ground pin of the mini DIN plug to give a feed to my Acom linear.
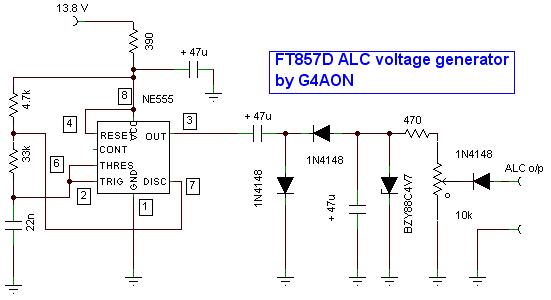

I've contacted Yaesu for their view on this problem and they apparently have a key click modification that is applied to the current FT857D series, from board 07 onwards. I couldn't determine which version mine was, lifting the main board didn't indicate it was modified or not. I sold the rig and didn't return it for attention by Yaesu, so cannot comment on whether the modification cures the problem or not.
Anyone wishing to modify their FT857 using the modification below does so at their own risk. While the modification was supplied by Yaesu, it doesn't make it easy to implement. The modification can be downloaded here .
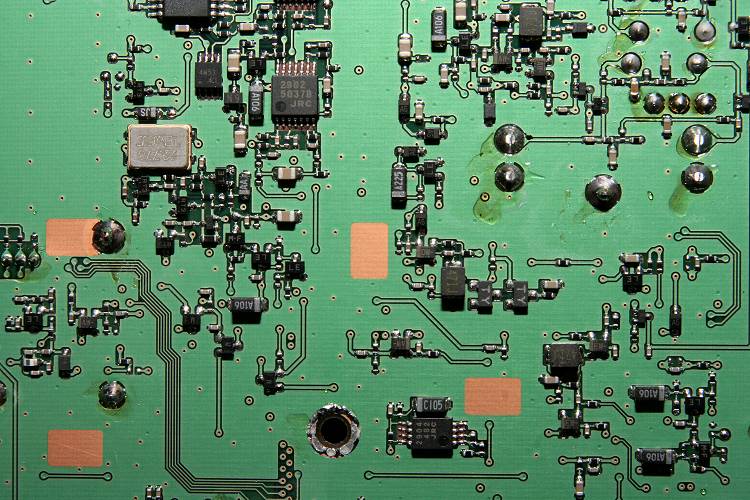
The central part of the underside of the main board in an FT857D is shown below (not modified).
I am indebted to Tom, W8JI, for pointing me in the direction of an external ALC voltage.

|
